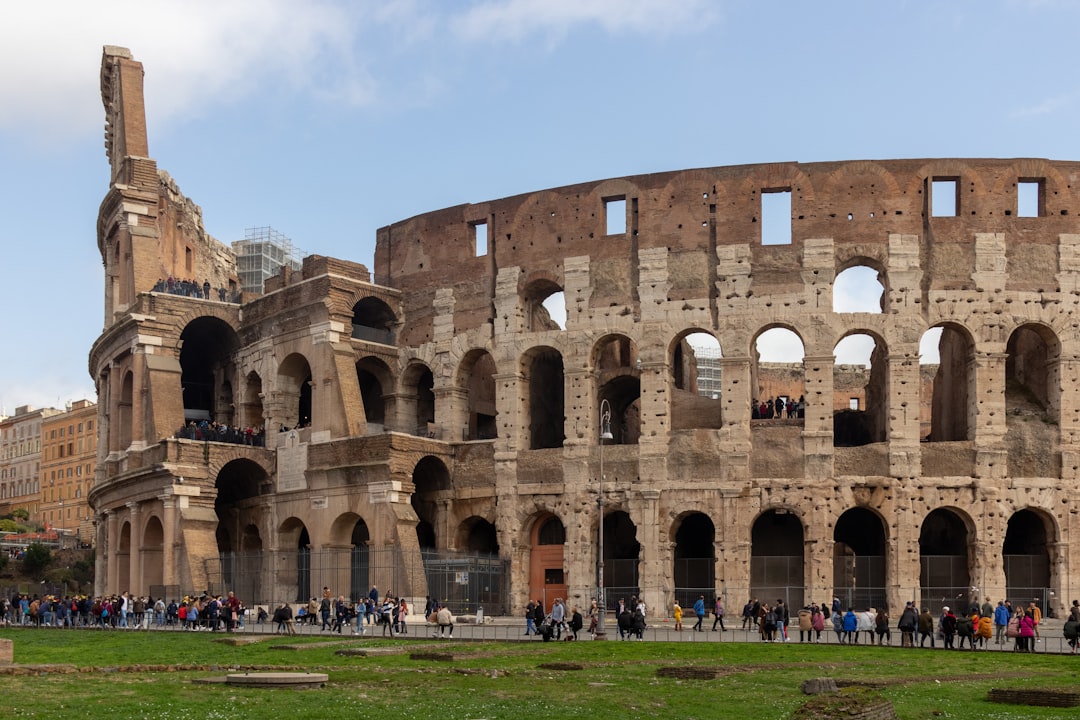
Monuments to Visit During Festivals: A Celebration of Culture and History
# Introduction. Festivals around the world offer a colorful tapestry of culture, traditions, and community celebrations. Amidst the festivities, various monuments stand as testament to history and culture, embodying the spirit of the events that take place around them. Visiting these monuments during festivals adds a unique dimension to the experience, allowing travelers to connect deeply with local traditions while appreciating the architectural marvels that have withstood the test of time. In this post, we’ll explore several remarkable monuments to visit during festivals globally. # 1. The Colosseum in Rome, Italy - A Timeless Venue for Gladiatorial Reenactments. The Colosseum stands as one of the most iconic structures of ancient Rome. During the Roman festivals such as the Ludi Romani, the Colosseum came alive with gladiatorial games, theatrical performances, and chariot races. Though modern interpretations of events are conducted, visiting the Colosseum during such times allows tourists to experience the nostalgia and grandeur of Rome's historical festivities. Visitors can enjoy thematic tours that include reenactments, guided narratives of ancient traditions, and interactive events amidst the backdrop of this magnificent monument. # 2. The Great Wall of China - Celebrating the Mid-Autumn Festival. Every autumn, the Mid-Autumn Festival fills the air with joy and mooncakes. The Great Wall of China offers an extraordinary sight where families and friends gather to appreciate the full moon while exploring this UNESCO World Heritage Site. Events held here include lantern displays, traditional music, and cultural performances that celebrate unity and harvest. Visiting the Great Wall during the festival is an unforgettable experience, allowing for both appreciation of the wall’s historical significance and participation in modern festivities. # 3. The Eiffel Tower in Paris, France - Bastille Day and Fireworks. The Eiffel Tower is synonymous with Parisian romance and culture. Every July 14th, on Bastille Day, the tower is the epicenter of celebrations, culminating in a stunning fireworks display. The monument is illuminated, and many festivities, including parades and street fairs, surround it. Visitors can enjoy live music, dancing, and exquisite French cuisine while soaking in the lively atmosphere. This iconic landmark adds a layer of grandeur to the festivities, making it a must-visit during the holiday festivities. # 4. The Pyramids of Giza - Celebrating the Cairo International Festival of Contemporary Dance. Home to one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, the Pyramids of Giza become a significant cultural hub during the Cairo International Festival of Contemporary Dance. With performances set against the backdrop of the pyramids, the festival features a mix of local and international artists showcasing dance forms inspired by Egyptian history and culture. The juxtaposition of ancient architecture and modern art makes it a fascinating spectacle, drawing both history enthusiasts and art lovers to this monumental site. # 5. The Taj Mahal in Agra, India - Taj Mahotsav and Cultural Extravaganza. The Taj Mahal, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a symbol of love, plays host to the Taj Mahotsav, a 10-day festival celebrating Indian culture. The monument not only mesmerizes with its architectural beauty but also transforms into a cultural melange where artisans, dancers, and performers congregate. The event highlights crafts, local cuisines, and traditional music, allowing visitors to indulge in India's rich heritage while marveling at the majestic Taj Mahal. It’s an excellent opportunity to appreciate both this historical monument and the vibrancy of Indian culture. # 6. Machu Picchu - Inti Raymi: Festival of the Sun. Machu Picchu offers more than breathtaking landscapes and archaeological wonder; it hosts the Inti Raymi, the Festival of the Sun, in June each year. Ancient Incan traditions come alive as locals and tourists alike gather for exuberant reenactments of worship rituals to the sun god Inti. Thousands participate in traditional music, dance, and ceremonies that evoke a deep appreciation for Incan culture. Visiting Machu Picchu during the festival is an incredible way to experience the intersection of history, spirituality, and community celebration within Andes' magnificent landscape. # Conclusion. Visiting monuments during festivals provides an opportunity to deeply engage with local culture and history. The intertwining of monumental architecture and community celebrations creates a vibrant atmosphere that helps travelers appreciate traditions while witnessing the historical context of these landmarks. Whether it’s the grandeur of the Colosseum or the ethereal beauty of the Taj Mahal, participating in these cultural events offers an enriching experience that honors both the past and the present. Plan your travel around these incredible festivals to not just see monuments, but to truly experience the heart of diverse cultures around the world. .